🧬 Understanding Selective Receptor Modulation in Research
Selective receptor modulation is a core concept in modern biochemical and pharmacological research. By studying how specific compounds interact with targeted receptors, scientists gain valuable insight into cellular signaling, gene expression, and pathway regulation.
In research settings, selective receptor modulation allows laboratories to explore mechanism-driven effects without broadly activating or inhibiting entire biological systems. This precision makes receptor modulation studies essential in preclinical research, molecular biology, and drug discovery.
What Is Selective Receptor Modulation?
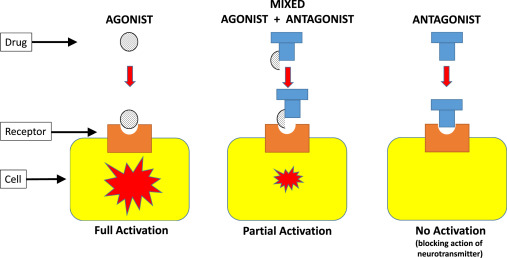
Selective receptor modulation refers to the ability of a compound to bind to a specific receptor subtype and influence its activity in a controlled and pathway-dependent manner.
Rather than fully activating or blocking a receptor, modulators may:
- Enhance receptor activity in certain tissues
- Reduce signaling in others
- Trigger selective downstream pathways
This selectivity enables researchers to study receptor behavior with greater specificity than traditional agonists or antagonists.
Why Receptor Selectivity Matters in Research
Receptors often exist in multiple tissues and cell types. Non-selective compounds can produce confounding results due to off-target activity.
Selective modulation allows researchers to:
- Isolate specific signaling pathways
- Reduce experimental noise
- Improve reproducibility across studies
- Better understand receptor-dependent mechanisms
This makes selective receptor modulation a powerful research strategy.
Key Receptors Studied in Modulation Research
Selective receptor modulation research commonly focuses on:
Androgen Receptors
Studied in cellular signaling, gene transcription, and metabolic pathway research.
Estrogen Receptors
Used in investigations of receptor subtype activity and tissue-specific signaling.
Nuclear Hormone Receptors
Important for understanding transcription regulation and intracellular signaling.
Neuroreceptors
Researched in synaptic signaling and neurotransmitter pathway studies.
Each receptor system offers insight into complex biological regulation mechanisms.
Research Applications of Selective Receptor Modulators
Selective receptor modulators are used in laboratories for:
1. Receptor Binding Studies
- Measuring binding affinity
- Mapping receptor-ligand interactions
- Identifying structure-activity relationships (SAR)
2. Signal Transduction Research
- Studying downstream signaling cascades
- Evaluating pathway-specific activation
- Comparing receptor response profiles
3. Preclinical Research Models
- Investigating receptor behavior in controlled systems
- Supporting early-stage drug discovery research
- Validating hypotheses before clinical development
Role of Research Chemicals in Modulation Studies
Research chemicals used in receptor modulation studies must meet strict quality standards. Laboratories rely on compounds that offer:
- High purity (≥98–99%)
- Verified identity via COA documentation
- Consistent batch-to-batch performance
Even trace impurities can alter receptor binding data, making quality sourcing essential.
Analytical Methods Used in Receptor Modulation Research
Common analytical techniques include:
- Radioligand binding assays
- HPLC and LC-MS for purity verification
- Cell-based assays for functional response
- Gene expression analysis to track transcription changes
These tools allow researchers to quantify and compare receptor interactions with precision.
Storage, Handling & Compliance
Selective receptor modulators are research-grade compounds and must be handled responsibly:
- Store under recommended temperature and light conditions
- Use airtight, labeled containers
- Maintain COA and batch documentation
- Follow all laboratory safety protocols
All compounds must be used strictly for research purposes and never for human or animal consumption.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
Receptor modulation research requires clear boundaries:
- No therapeutic or performance claims
- Use limited to laboratory and analytical research
- Compliance with chemical safety and transport regulations
Responsible handling protects both scientific integrity and institutional compliance.
Conclusion
Selective receptor modulation is a cornerstone of modern research, enabling scientists to explore biological signaling with exceptional precision. Through controlled receptor-ligand interactions, laboratories gain deeper insight into molecular mechanisms, pathway regulation, and receptor dynamics.
By using high-purity research chemicals, verified documentation, and robust analytical methods, researchers can conduct reliable, reproducible, and ethically sound receptor modulation studies.